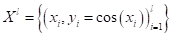- Decision Tree using CART algorithm Solved Example 2
- Download Final Year Projects
- Decision Tree using CART algorithm Solved Example 2 – Loan Approval Data Set
- Solution:
- Right subtree,
- Решающие деревья в задачах регрессии. Алгоритм CART
- Реализация решающих деревьев на Python с помощью Scikit-Learn
- CART Decision Tree Python Example
- What is CART & How does it work?
- CART Decision Tree Python Example
- Conclusion
- Ajitesh Kumar
Decision Tree using CART algorithm Solved Example 2
Download Final Year Projects
Decision Tree using CART algorithm Solved Example 2 – Loan Approval Data Set
In this tutorial, we will understand how to apply Classification And Regression Trees (CART) decision tree algorithm (Solved Example 2) to construct and find the optimal decision tree for the given Loan Approval Data set. Also, predict the class label for the given example…?
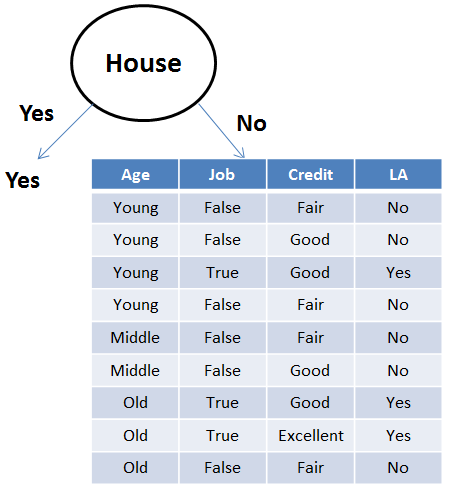
| Age | Job | House | Credit | Loan Approved |
| Young | False | No | Fair | No |
| Young | False | No | Good | No |
| Young | True | No | Good | Yes |
| Young | True | Yes | Fair | Yes |
| Young | False | No | Fair | No |
| Middle | False | No | Fair | No |
| Middle | False | No | Good | No |
| Middle | True | Yes | Good | Yes |
| Middle | False | Yes | Excellent | Yes |
| Middle | False | Yes | Excellent | Yes |
| Old | False | Yes | Excellent | Yes |
| Old | False | Yes | Good | Yes |
| Old | True | No | Good | Yes |
| Old | True | No | Excellent | Yes |
| Old | False | No | Fair | No |
| Age | Job | House | Credit | Loan Approved |
| Young | False | No | Good | ? |
Solution:
Now, for the right subtree, we write all possible rules and find the total error. Based on the total error table, we will construct the tree.
Right subtree,
Consolidated rules, errors for individual attributes values, and total error of the attribute are given below.
| Attribute | Rules | Error | Total Error |
| Age | Young->No | 1/4 | 2/9 |
| Middle->No | 0/2 | ||
| Old->Yes | 1/3 | ||
| Job | False->No | 0/6 | 0/9 |
| True->Yes | 0/3 | ||
| Credit | Fair->No | 0/4 | 2/9 |
| Good->Yes/No | 2/4 | ||
| Excellent->Yes | 0/1 |
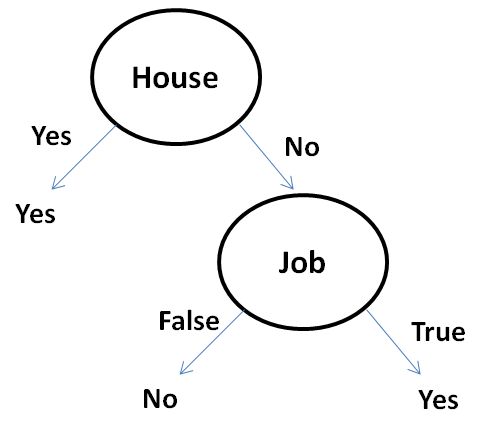
From the above table, we can notice that Job has the lowest error. Hence Job is considered as the splitting attribute. Also, when Job is False the answer is No as it produces zero errors. Similarly, when Job is True the answer is Yes, as it produces zero errors.
The final decision tree for the given Loan Approval data set is,
Also, from the above decision tree the prediction for the new example:
| Age | Job | House | Credit | Loan Approved |
| Young | False | No | Good | No |
In this tutorial, we understood, how to apply Classification And Regression Trees (CART) decision tree algorithm (solved example 2) to construct and find the optimal decision tree for the Loan Approval data set. If you like the tutorial share it with your friends. Like the Facebook page for regular updates and YouTube channel for video tutorials.
Источник
Решающие деревья в задачах регрессии. Алгоритм CART
На предыдущих занятиях мы с вами рассматривали решающие деревья для задач классификации. Однако, в ряде случаев, их применяют и для задач регрессии, когда алгоритм на выходе формирует одно вещественное значение (или несколько значений) для каждого входного вектора . То есть, в листьях такого дерева хранятся соответствующие вещественные числа.
Давайте, для определенности, я сразу приведу пример такого решающего дерева.
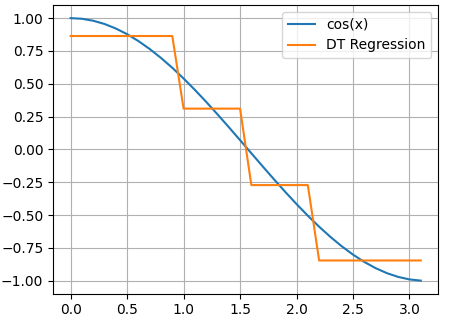
Смотрите, изначально наши данные представляют собой точки функции cos(x):
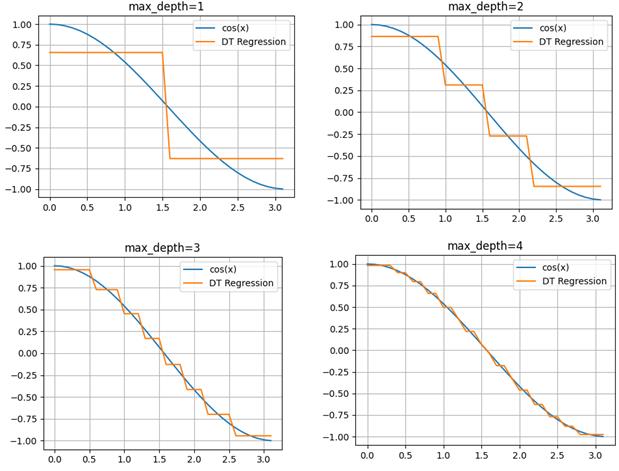
Здесь аргумент функции cos() – это признак, а значения функции в каждой точке – целевые переменные. Затем, по признаку (аргументу функции) выполняется разделение исходного множества точек на непересекающиеся подмножества. В результате, при глубине дерева два, получаем четыре подинтервала и четыре листа. Причем, в каждом листе хранится одно константное вещественное значение, которым заменяются все значения выделенного подмножества. Поэтому мы видим на графике ступенчатую функцию при аппроксимации косинусоиды решающим деревом.
Вот общая идея использования решающих деревьев для задач регрессии. И здесь возникают два главных вопроса:
- По какому критерию оценивать качество деления на подмножества (то есть, что использовать в качестве меры неопределенности – impurity)?
- Как вычислять вещественные значения в полученных листовых вершинах?
Хорошая новость, что на оба этих вопроса имеется единый ответ. Я начну с последнего. Часто в задачах регрессии требуется обеспечить минимум среднеквадратичной ошибки прогноза: 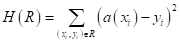
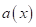
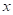
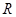
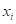
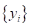
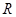
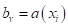
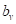
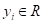
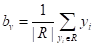
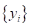
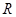
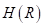
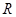
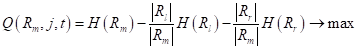
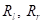
Реализация решающих деревьев на Python с помощью Scikit-Learn
Итак, мы с вами в целом познакомились с идеей решающих деревьев для задач классификации и регрессии. Осталось узнать, как можно реализовать эти подходы при решении практических задач. В самом простом варианте это можно сделать на языке Python с использованием библиотеки Scikit-Learn. В этой библиотеке имеется ветка:
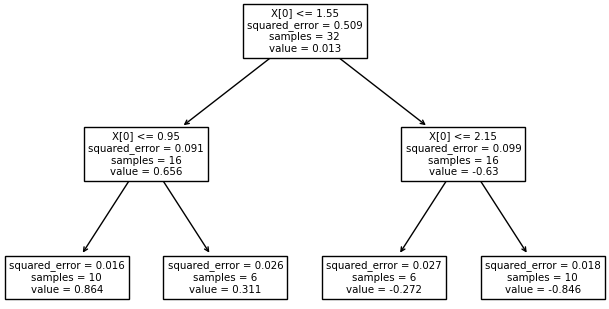
которая отвечает за построение решающих деревьев. Разработчики Scikit-Learn использовали алгоритм: Classification and Regression Trees (CART) с помощью которого можно выполнять как классификацию, так и решать задачи регрессии. Подробнее об этом можно почитать на странице официальной документации: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/tree.html Давайте, вначале построим решающее дерево для задачи регрессии. Для этого сформируем обучающее множество в виде значений функции косинуса:
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x = np.arange(0, np.pi, 0.1).reshape(-1, 1) y = np.cos(x)
clf = tree.DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=3) clf = clf.fit(x, y)
Источник
CART Decision Tree Python Example
The Classification and Regression Tree (CART) is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification, regression. In this blog, we will discuss what CART decision tree is, how it works, and provide a detailed example of its implementation using Python.
What is CART & How does it work?
CART stands for Classification And Regression Tree. It is a type of decision tree which can be used for both classification and regression tasks based on non-parametric supervised learning method. The following represents the algorithm steps. First and foremost, the data is split into training and test set.
- Take a feature K and split the training data set into two subsets based on some threshold of the feature, Tk. For example, if we are working through the IRIS data set, take a feature such as petal length, set the threshold as 2.25 cm. The question that would arise is how does the algorithm select K and Tk. The pair of K and Tk is selected in a way that purest subsets (weighted by their size) are created. This can also be called as the cost or loss function. The following cost function is optimized (minimized).
- Once the training set is split into two subsets, the algorithm splits the subsets into another subsets using the same logic.
- The above split continues in a recursive manner until the maximum depth (hyperparameter max_depth) is reached or the algorithm is unable to find the split that further reduces the impurity.
- The following are few other hyperparameters which can be set before the algorithm is run for training. These are used to regularize the model.
- min_samples_split: Minimum number of samples a node must have before it is split
- min_samples_leaf: Minimum number of samples a leaf node must have
- max_leaf_nodes: Maximum number of leaf nodes
CART decision tree is a greedy algorithm as it searches for optimum split right at the top most node without considering the possibility of lowest possible impurity several levels down. Note that greedy algorithms can result into a reasonably great solution but may not be optimal.
The following represents the CART cost function for regression. The cost function attempts to minimize the MSE (mean square error) for regression task. Recall that CART cost function for classification attempts to minimize impurity.
CART Decision Tree Python Example
Scikit-Learn decision tree implementation is based on CART algorithm. The algorithm produces only binary trees, e.g., non-leaf nodes always have two children. There are other algorithms such as ID3 which can produce decision trees with nodes that have more than two children .
The following is Python code representing CART decision tree classification.
import pandas as pd from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn import metrics from sklearn import datasets #load IRIS dataset iris = datasets.load_iris() X = iris.data #load the features y = iris.target # load target variable # Split dataset into training set and test set X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1) # 70% training and 30% test # Create Decision Tree classifer object clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=2) # Train Decision Tree Classifer clf = clf.fit(X_train,y_train) #Predict the response for test dataset y_pred = clf.predict(X_test) # Model Accuracy, how often is the classifier correct? print("Accuracy:",metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)) You can then print the decision tree trained in the above code using the following code:
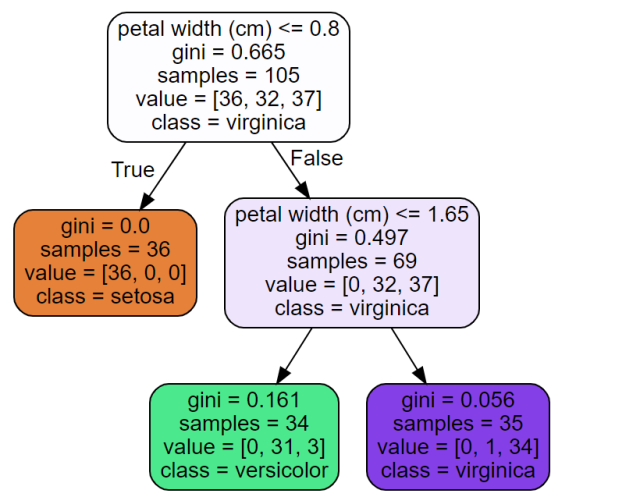
from sklearn.tree import export_graphviz import os # Where to save the figures PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = "." def image_path(fig_id): return os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT_DIR, "sample_data", fig_id) export_graphviz( clf, out_file=image_path("iris_tree.dot"), feature_names=iris.feature_names, class_names=iris.target_names, rounded=True, filled=True ) from graphviz import Source Source.from_file("./sample_data/iris_tree.dot") Executing the above code will print the following. Recall that scikit-learn decision tree (CART) implementation always produces binary trees.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CART decision trees are powerful supervised learning algorithms that can be used for both classification and regression tasks. The loss function for CART classification algorithm is minimizing the impurity while loss function for CART regression algorithm is minimizing mean square error (MSE).
Ajitesh Kumar
I have been recently working in the area of Data analytics including Data Science and Machine Learning / Deep Learning. I am also passionate about different technologies including programming languages such as Java/JEE, Javascript, Python, R, Julia, etc, and technologies such as Blockchain, mobile computing, cloud-native technologies, application security, cloud computing platforms, big data, etc. For latest updates and blogs, follow us on Twitter. I would love to connect with you on Linkedin. Check out my latest book titled as First Principles Thinking: Building winning products using first principles thinking
Источник